Intravenous (IV) treatments, as we know them today, have actually been around since 1950. The advent of plastics in the 1940s paved the way for the Rochester plastic needle, the first modern catheter device, which was developed at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Since 1950, intravenous therapies have proven highly safe. However, medical accidents can occur, and an IV-related mishap can lead to a blown vein.
What is a blown vein? How do you know if you have one? And what could be done about it? If you or a loved one is scheduled for IV therapy soon, these are important questions to answer.
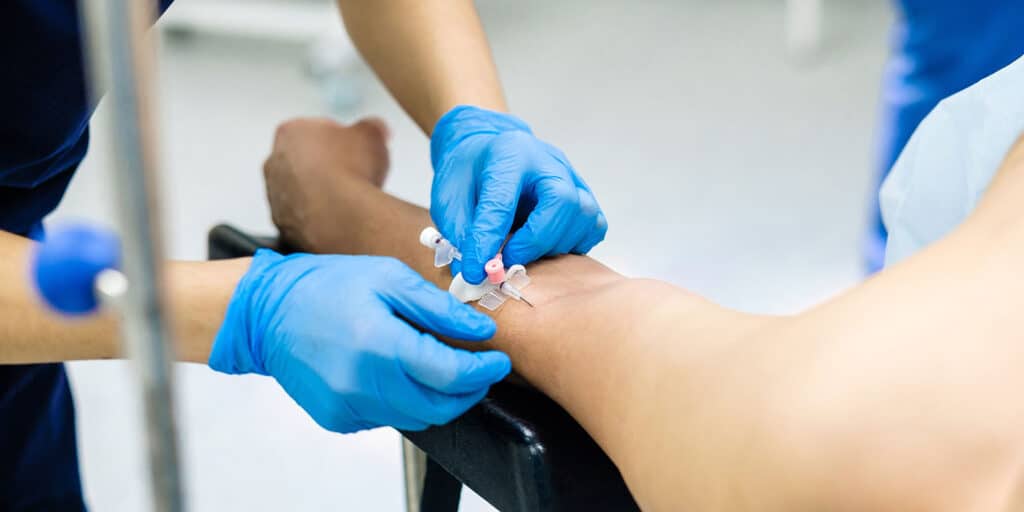
Table of Contents
Understanding IV Therapy
To begin with, IV Fluid therapies have numerous uses. They can transfer blood or blood draws and administer painkillers. IV insertion can also deliver fluids to someone who’s dehydrated. And they can supply special nutrients, supplements, or drugs to patients (IV drug use). For example, people who have cancer sometimes receive vitamin C intravenously.
In such cases, IV therapy provides fluids, nutrients, and medicine to patients who couldn’t accept them any other way — or who’d have a difficult time doing so. In fact, when these materials enter a person’s system via a vein, they bypass the digestive system completely.
To provide traditional IV therapy, medical professionals first pierce a patient’s skin — usually through the soft inner part of the elbow — with a needle or needle insertion. They next insert a small tube called a cannula through the injection site or insertion site and into a vein wall.
The other end of the cannula connects to a larger tube, and that bigger tube is attached to an IV bag. The IV bag holds the specific substances that the patient needs, and they drip down into the vein.
What is a Blown Vein?
During a proper injection, the needle’s tip penetrates the vein’s wall, and it stops in the lumen. A lumen is the passageway of a blood vessel through which blood flows.
However, on occasion, a medical provider inserts the needle a little too far, and its tip pokes through the other side of the vein. When that happens, the vein might be ruptured vein–this injury is known as a blown vein which could result in vein damage if neglected.
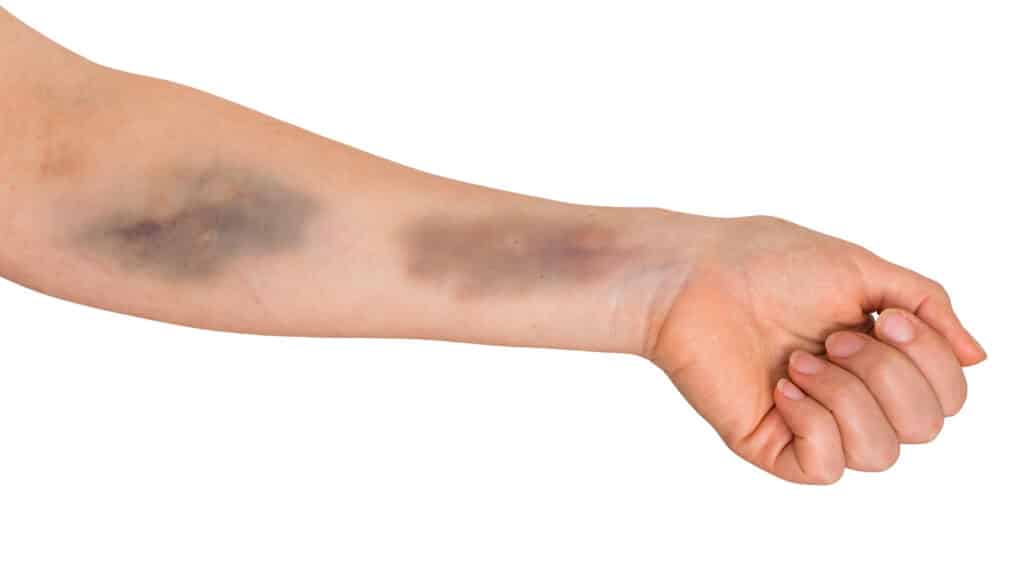
In most cases, a blown vein isn’t a serious health concern at all. The patient will just get a fairly large bruise called a hematoma. A hematoma occurs when some portion of leaking blood from a blood vessel pools just below the skin.
Typically, this bruise is mildly uncomfortable, but it will start clearing up in a few days. Then it’ll be totally gone within 10 to 12 days. At that point, a healthcare professional could pierce that same vein again.
Many times, medical providers realize right away that a patient has a blown vein. In such an instance, they’ll try to lessen the blood loss by pressing down on the injection area. They’ll also sterilize that part of the body so that it won’t get infected. And, if there’s any swelling, they might apply ice pack to the area.
Causes of a Blown Vein
Various factors make a blown vein more likely to occur.
For one thing, a healthcare provider might use a needle that’s too large for the vein. Or the needle might enter the vein at an incorrect angle. In fact, even if that angle is off just slightly, it can lead to a blown vein.
In addition, if a patient moves at all during an injection, it can knock the needle off target. Sometimes — perhaps due to a fear of needles or medical procedures in general — people unintentionally twitch at exactly the wrong moment.
On top of that, some veins are especially susceptible to this kind of injury. For example, veins can become more fragile with age or after multiple injections. And some veins move a little to the side whenever they’re touched; they’re called rolling veins. Fragile veins and rolling veins are both more likely to rupture.
Complications of a Blown Vein
Blown veins sometimes cause pain, swelling, numbness, or skin tightness in the affected area.
In rare instances, a blown vein will cave in, preventing blood from passing through. This situation is called a collapsed vein, and it will usually heal on its own.
Some collapsed veins never get better, though. And there’s no way to treat a collapsed vein that won’t heal.
A person’s body will make up for a permanent collapsed vein by redirecting blood into smaller nearby veins. Furthermore, the body will absorb that collapsed vein; it will, in essence, vanish. And, once blood starts going through those smaller veins, varicose veins often become visible on the skin.
Prevention Strategies
The first key to preventing a blown vein is to be open with your healthcare professionals. Let them know if you’ve ever fainted during an injection or if you’re uncomfortable around needles. They might have you lie flat on your back or close your eyes during your injection. That way, you can stabilize yourself more effectively.
Your healthcare professional might also touch your vein before injecting it, just to make sure it isn’t a rolling vein.
Moreover, unless your medical facility instructs you otherwise, drink plenty of fluids in the 24 hours before your injection. (A healthy amount is about 11.5 cups for women and 15.5 for men.) Avoid caffeine during that period as well. If you’re well-hydrated, it’s easier for your caregiver to find the right vein to inject.
Note that, these days, some hospitals and clinics have started utilizing needle-free IV systems. If that technology eventually gains widespread usage, it could greatly curtail blown veins. Until that day, though, taking the right precautions could help you to avoid this nettlesome issue.
Finally, to learn more about blown veins and IV therapies more broadly, please contact the Garden State Treatment Center, a treatment center at any time. We’re always here to help you and your loved ones with tailored treatment options, especially for you and for further treatment.
FAQ
How do you treat a blown vein?
Sources
- courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-ap2/chapter/structure-and-function-of-blood-vessels/#:~:text=Each%20type%20of%20vessel%20has,blood%20moving%20through%20the%20system.
- www.health.harvard.edu/blog/drip-bar-should-you-get-an-iv-on-demand-2018092814899
- www.ivwatch.com/2020/11/10/the-history-of-iv-therapy
- www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/blown-vein#is-it-serious
- my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24599-blown-vein
- myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/aftercareinformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=zx4360#:~:text=A%20hematoma%20is%20a%20bad,does%20not%20cause%20blood%20clots.
Published on: 2023-12-27
Updated on: 2025-02-07



